

Your health care provider might discourage amniocentesis if you have an infection, such as HIV/ AIDS, hepatitis B or hepatitis C. Earlier than 32 weeks, a baby's lungs are unlikely to be fully developed.Īmniocentesis isn't appropriate for everyone, however. It's usually done between 32 and 39 weeks of pregnancy. This type of amniocentesis is done only if early delivery - either through induction or C-section - is being considered to prevent pregnancy complications for the mother in a nonemergency situation. Your health care provider might recommend amniocentesis to diagnose or rule out genetic conditions associated with abnormal ultrasound findings.įetal lung maturity amniocentesis can determine whether a baby's lungs are ready for birth. You have abnormal ultrasound findings.In addition to identifying Down syndrome and the neural tube defect spina bifida, amniocentesis can be used to diagnose many other genetic conditions - such as cystic fibrosis. You have a family history of a specific genetic condition, or you or your partner is a known carrier of a genetic condition.Your health care provider might suggest amniocentesis to rule out these conditions. Babies born to women 35 and older have a higher risk of chromosomal conditions, such as Down syndrome.
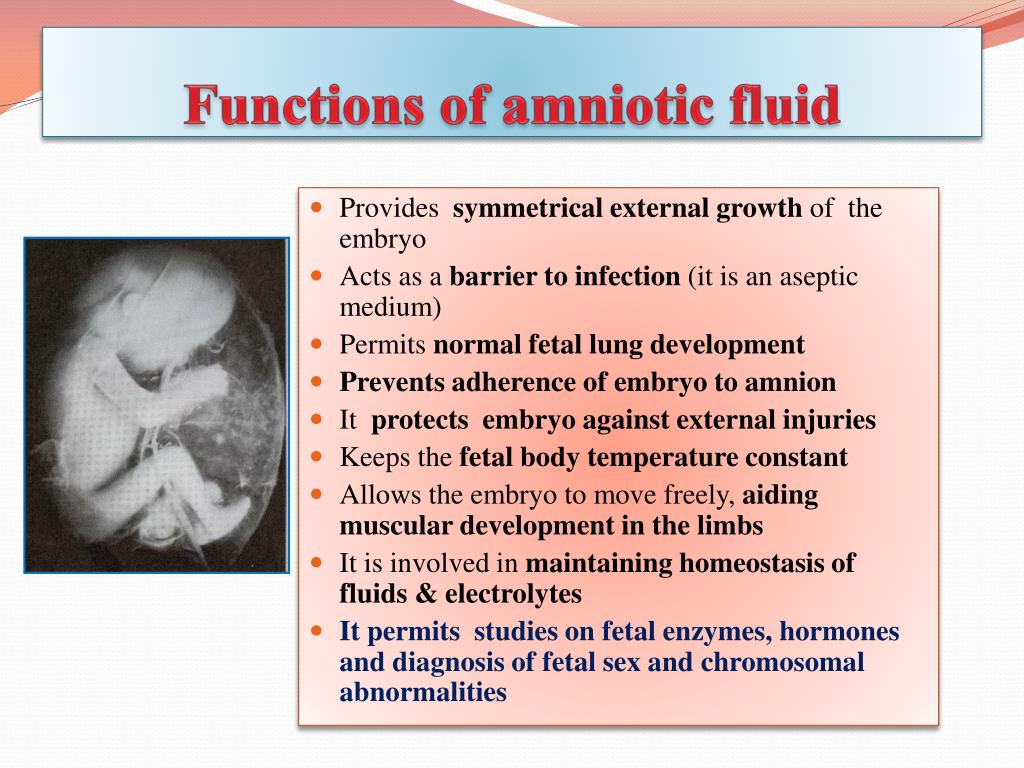
If a previous pregnancy was affected by conditions such as Down syndrome or a neural tube defect - a serious condition affecting a baby's brain or spinal cord - your health care provider might suggest amniocentesis to confirm or rule out these disorders.


Generally, genetic amniocentesis is offered when the test results might have a significant impact on the management of the pregnancy or your desire to continue the pregnancy. Genetic amniocentesis can provide information about your baby's genetic makeup. Amniocentesis can collect DNA from the fetus that can then be compared to DNA from the potential father. If you accumulate too much amniotic fluid during pregnancy (polyhydramnios), amniocentesis might be done to drain excess amniotic fluid from your uterus. The procedure can also be done to evaluate the severity of anemia in babies who have Rh sensitization - an uncommon condition in which a mother's immune system produces antibodies against a specific protein on the surface of the baby's blood cells. Occasionally, amniocentesis is used to evaluate a baby for infection or other illness. Fetal lung maturity testing involves taking a sample of amniotic fluid and testing it to determine whether a baby's lungs are mature enough for birth. Genetic amniocentesis involves taking a sample of amniotic fluid and testing it for certain conditions, such as Down syndrome. Amniocentesis can be done for various reasons:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
